
June 2021
Accounting standards applicable to future group benefits:
Assumptions used by Canadian organizations
Several private sector organizations must include the recognition of their obligations toward defined benefit pension plans (DB pension plans) and group benefits plans offered to retirees (other benefits) in their financial statements.
Again this year, Normandin Beaudry’s specialists analyzed the annual reports of Canadian organizations listed on the S&P 60 Index (60 largest organizations) and the S&P MidCap Index (mid-cap organizations), the fiscal year of which ended between September 30, 2020, and February 28, 2021.
This analysis included about 60 organizations from the S&P 60 Index and the S&P MidCap Index that sponsor at least one DB pension plan. Of these organizations:
- 66% offer at least one medical care plan to their retirees; and
- 84% disclose their results in accordance with international accounting standards, while the others disclose them in accordance with U.S. accounting standards.
The following charts present the key economic assumptions used by the organizations analyzed for their DB pension plans and other benefits. The assumptions are those that were in effect at the end of the fiscal year considered and used to calculate the obligation at the end of the fiscal year.
Each chart presents the historical evolution of the assumptions. Medians are represented by a solid line and shaded floating bars represent the range from the fifth percentile to the ninety-fifth percentile.
The discount rate is one of the most important assumptions. Because it is based on market rates, it can vary from month to month. The discount rate can also vary depending on the methodology used to determine the market rate, the plan’s maturity profile and the duration of the coverage offered upon retirement (for example, a lump sum amount upon retirement or annual payments until age 65 rather than lifetime benefits). The sensitivity of the obligation to the discount rate movement depends on its duration. For example, for the same 0.1% decrease in the discount rate:
- A plan offering lifetime coverage, the obligation duration of which is 10 years, will see its obligation increase by 1%
- A plan offering lifetime coverage, the obligation duration of which is 20 years, will see its obligation increase by 2%
The following chart presents the historical evolution of the discount rates for DB pension plans and other benefits.
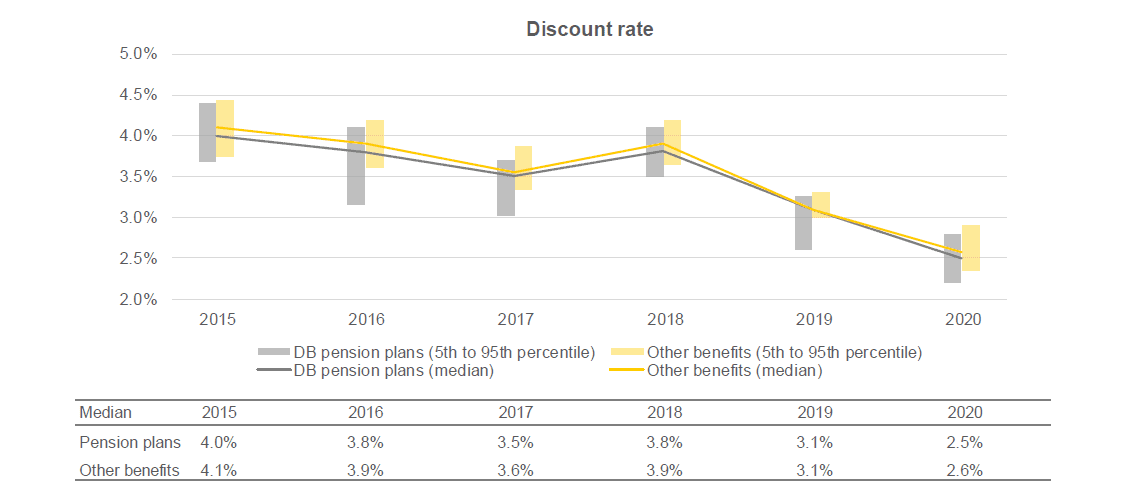
- Since the publication of the 2019 year-end results, the discount rate has fluctuated significantly from month to month, to finish out 2020 at its lowest level in the past few years.
- About 50% of the organizations analyzed used a discount rate identical to the one used for DB pension plans for other benefits.
Many of the organizations analyzed sponsor DB pension plans and other benefits that offer benefits based on salary at retirement. These organizations must therefore establish an assumption related to the compensation growth rate of active members.
The following chart presents the historical evolution of compensation growth rates.
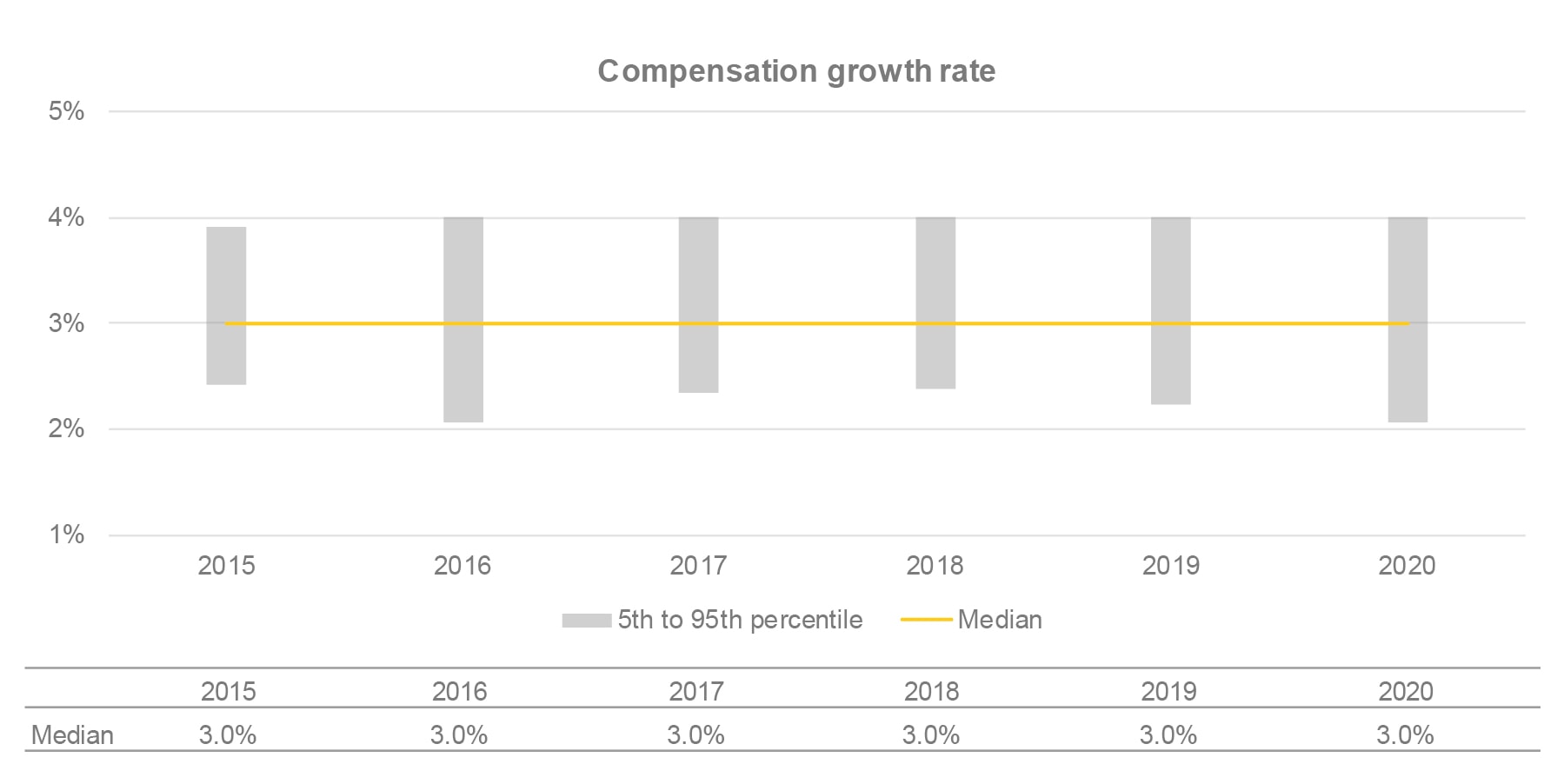
- Assumptions for the compensation growth rate for accounting recognition purposes have been stable for several years.
The growth rate of medical care costs is an important assumption for group benefits plans offered to retirees, as it shapes the future level of costs and its growth is higher than overall inflation.
Most organizations use an initial rate that decreases over a specified period into a final rate, which will apply in subsequent years. The initial rate can vary significantly from one organization to another, compared to the final rate, which usually varies less.
The following chart presents the historical evolution of the initial and final growth rates of medical care costs.
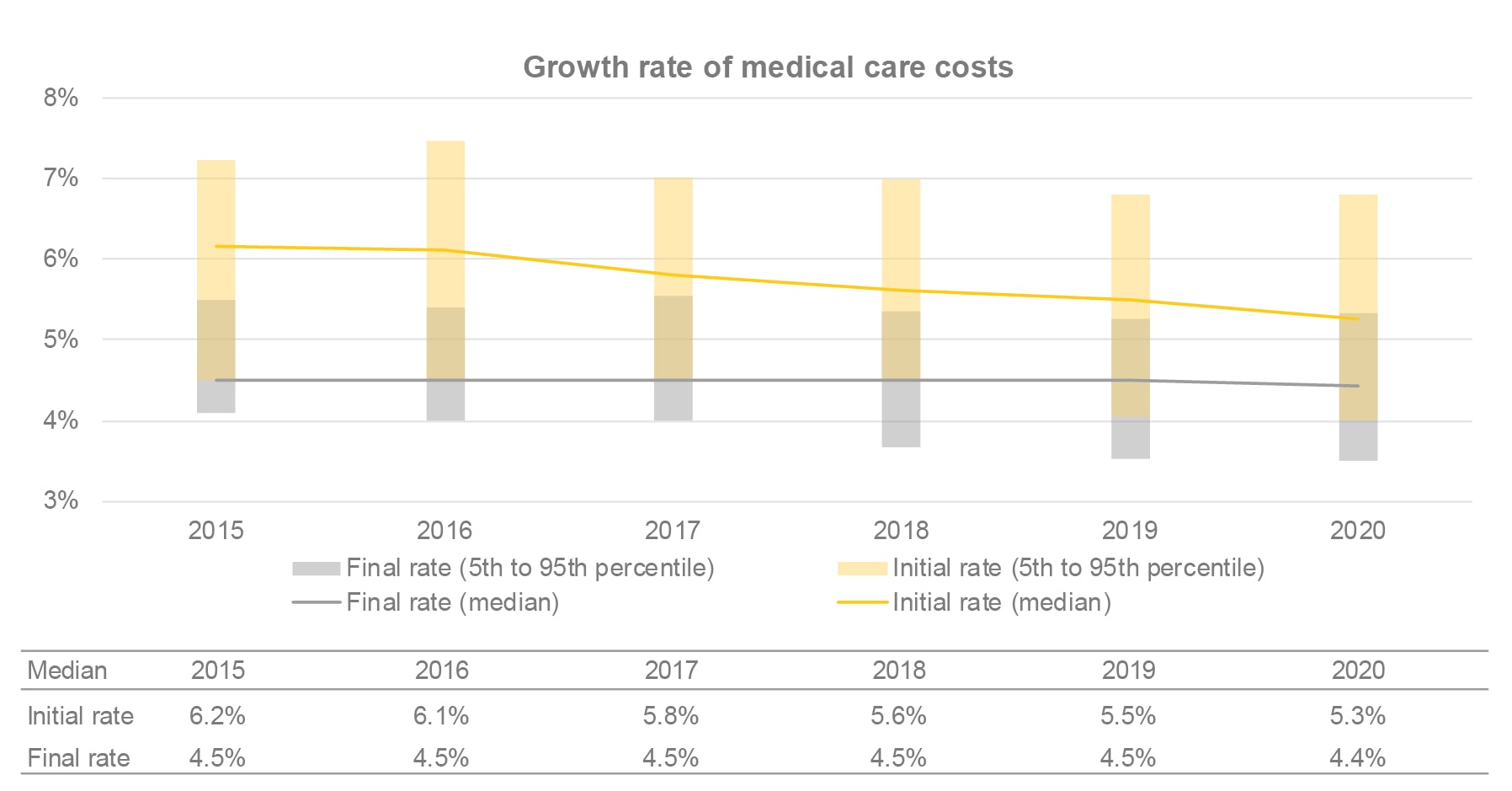
- In recent years, there has been a general downward trend in the growth rates of medical care costs.
- The timeframe to reach the final rate can also vary significantly from organization to organization. At the end of 2020, 73% of organizations that offer at least one medical care plan to their retirees use decreasing rates, over a period ranging from 10 to 20 years for most organizations.
In 2016, the Public Sector Accounting Board (PSAB) started a project on employment benefits to examine Sections PS 3250 and PS 3255 and eventually publish a new section. At the end of March 2021, the PSAB approved the exposure draft, “Employee Benefits, Proposed Section PS 3251,” and the accompanying basis for conclusions. The Board expects to issue the document in July 2021, with comments due in November 2021. The proposed Section PS 3251 will replace existing Sections PS 3250 and PS 3255.
For several years, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) has been working on a project to improve the usefulness of the information to be provided in financial statement disclosures. This project is in response to a consultation that allowed primary users to express their concerns regarding current disclosure requirements, which led to issues such as the lack of relevant information, surplus of irrelevant information, and ineffective communication of the information.
As a result, in March 2021, IASB published an exposure draft entitled, “Disclosure Requirements in IFRS Standards – A Pilot Approach,” which proposes new guidelines for preparing and drafting more adequate disclosure requirements (for all its standards) in the future. In its pilot project, IASB proposed to replace the disclosure requirements for employee benefits (Section IAS 19) and those included in its standard on fair value measurement (Section IFRS 13). The proposed changes would require companies to comply with disclosure objectives and apply judgment to decide what to disclose. Comments are due in October 2021.
Below are some examples of proposed changes:
- Any entity with defined benefit plans would be required to apply judgment to determine the information about the nature of risks associated to their plans that is most useful to users of financial statements in the entity’s particular case, thus focusing its disclosures on material information.
- Any entity with defined benefit plans would be required to present a quantitative executive summary of their plans to improve communication effectiveness.
- For defined benefit plans that are closed to new members, an entity would be required to focus its disclosures on communicating how long defined benefit plans that are closed to new members will continue to affect the entity.
On November 1, 2020, the Accounting Standards Board (AcSB) published the final text presenting the changes announced to Section 3462 (“Employee Future Benefits”) regarding the use of going concern valuations. You can consult our bulletin from last November for a summary of the changes regarding the use of going concern valuations for private enterprises and private sector not-for-profit organizations. The changes will apply to fiscal years starting on or after January 1, 2022. Early adoption is permitted.
Our specialists assist many clients in preparing their financial statements. We can help you comply with accounting standards. Contact us!
